Designs
What is a design?
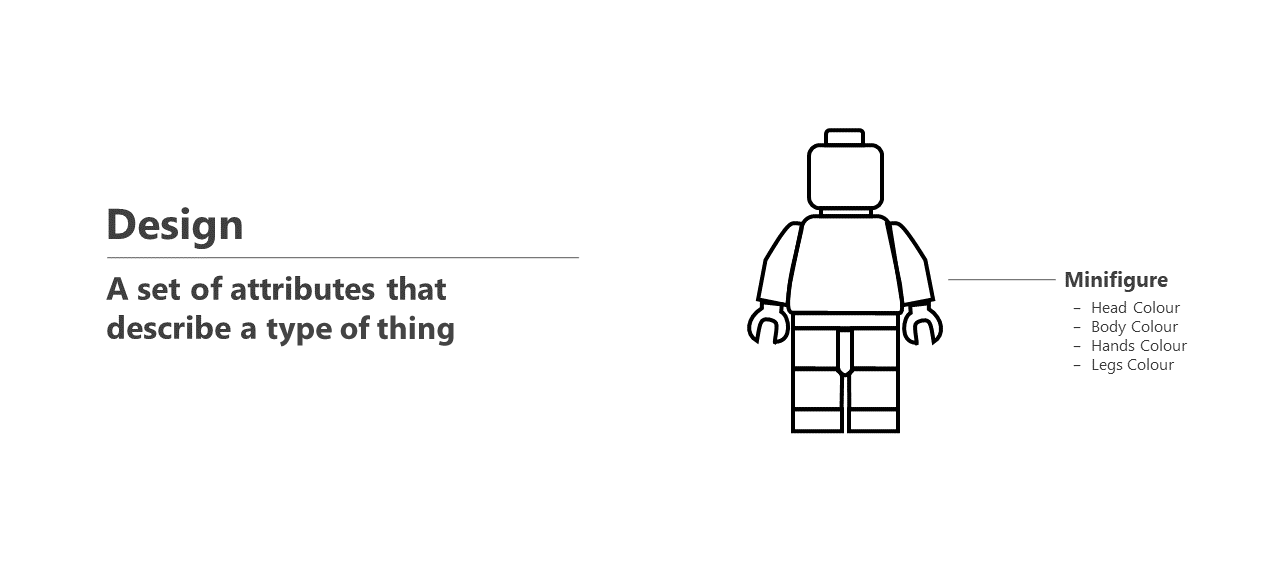
Designs are fundamental to the data structure of CausewayOne Asset Management. A design is a set of attributes that collectively describe a type of thing, such as an asset type (e.g. Street Lights) or an activity type (e.g. Highway Inspections). To store data about an actual thing (e.g. a specific street light), you can create an item of the design, which stores one set of values for those attributes.
If you're familiar with conventional databases, you can think of a design as the schema that defines the columns of a table. Each item of the design is a row of values.
For example, the design illustrated below describes a minifigure. It contains colour attributes for the Head, Body, Hands and Legs. The design contains no values, it just defines the possible data variables that can be stored about minifigures.
Due to their similarities, designs and interfaces are sometimes referred to as DoDIs. This stands for Design or Design Interface.
Attributes
A design can have any number of defined attributes. It can also inherit attributes from interfaces.
An attribute is a data field that represents a single characteristic of the concept described by the design. The characteristic can be physical (e.g. dimensions, location) or abstract (e.g. unit number, installed date).
Link attributes are a special type that can reference items of a particular design/interface (e.g. the Teams design has a Members attribute that links to the Team Members design). This makes it possible for items to link to other items!
Attributes can be configured as Required, so that a value must be entered when creating or editing an item of the design. Attributes can also be configured with a default value, which gets set automatically on items but can be edited as needed.
To learn more, see Attributes in the Designer app.
To customise the order and visibility of item attributes in different scenarios, see Item forms in the Designer app.
Appearance
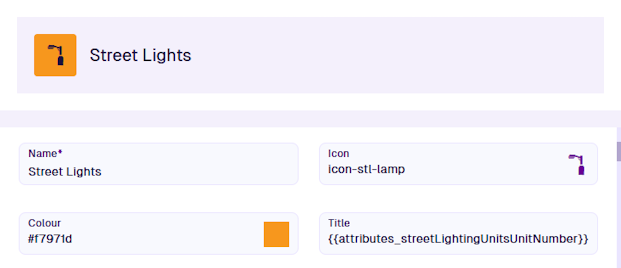
Every design has Icon and Colour properties. They define the visual identity of the design and its items. This makes items more recognisable when displayed in a list or on the map. They can be overridden on individual items as needed.
Additionally, every design has Title and Subtitle properties. They define how the primary and secondary labels of each item are generated. They can include text, attribute values, and even conditional logic to display context-sensitive information!
For example, asset designs typically display a unique attribute in the title and the design's name in the subtitle.
To learn more, see Titles and subtitles in the Designer app.
Geometry types
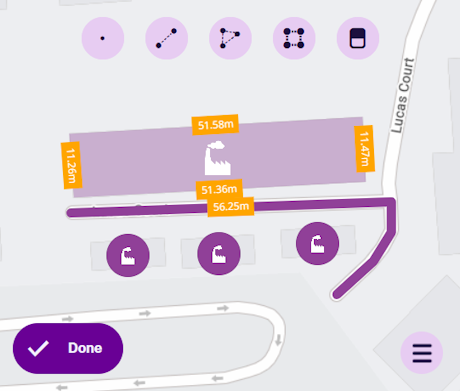
Every design has a Geometry attribute that can store coordinate data. This lets you record an item's location and shape. By default, the attribute is optional and accepts all geometry types (e.g. point, line, polygon).
Alternatively, you can configure a design's properties to make geometry Required, so that a value must be entered when creating/editing items of the design. You can also limit the types of geometry that can be stored, including none at all!
To learn more, see the Details section in the Designer app.
Context
Every design has a Context property that indicates its origin. If set to Customer, it was created by your organisation and can be edited freely. Otherwise, it's a protected system design.
System designs are included to provide core functionality and help you get started (e.g. the Teams and Team Members designs). While system designs can't be edited or deleted, they can be extended with extra attributes.
Details
The possible context types are:
-
Core - the design is included with CausewayOne Asset Management. It is required for system functionality, so it can't be deleted. However, you can:
-
edit these properties: Name, Icon, Colour, Title, Subtitle
-
add, edit or remove any custom attributes
-
implement or remove any extra interfaces
-
-
Module - the design belongs to an optional module. Same restrictions as Core.
-
Package - the design was created by our system architects as part of a custom solution for your organisation. Same restrictions as Core.
-
Customer - the design was created by your organisation. Therefore, you can freely edit or delete it, providing your user account has permission to do so.
If you create an item of a Core, Module or Package design, the item's context will be Customer!
Learn more
To learn more about creating and configuring designs, see Designs and interfaces in the Designer app.